Preventing and Combating Corruption
The OSCE participating States have recognized that “corruption represents one of the major impediments to the prosperity and sustainable development of the participating States that undermines their stability and security and threatens the OSCE’s shared values.”[quote from MC Decision No. 11/04]. Based on the mandate given by its participating States, the OSCE supports national authorities in implementing commitments under relevant international instruments and standards to prevent and combat corruption, in particular the United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) an the OECD’s Istanbul Anti-Corruption Action Plan. The OSCE also provides a platform for dialogue on political and security issues and it is uniquely positioned to support co-operation among its participating States in implementing and enforcing anti-corruption models and mechanisms.
Mandate
Since 1999, the OSCE has adopted several strategic and policy commitments, namely:
- Maastricht OSCE Strategy Document for the Economic and Environmental Dimension (2003)
- Sofia MC Decision No. 11/04 on Combating Corruption
- 2012 Dublin Ministerial Declaration on Strengthening Good Governance and Combating Corruption, Money-Laundering and the Financing of Terrorism
- Basel Decision No. 5/14 on Corruption Prevention
- Hamburg 2016 MC Decision No. 4/16 on Strengthening Good Governance and Promoting Connectivity
- Vienna MC Decision No. 8/17 on Promoting Economic Participation in the OSCE Area
- Milano MC Decision No. 5/18 on Human Capital Development in the Digital Era which showed strong political commitment and enhanced the mandate of the OSCE to promote good governance, combat corruption money-laundering and terrorism financing
The role of the OSCE
The OSCE work in anti-corruption is guided by the 2003 Maastricht OSCE Strategy Document for the Economic and Environmental Dimension, as well as relevant Ministerial Council Decisions of 2004 in Sofia, 2014 in Basel, 2016 in Hamburg, as well as a 2012 OSCE Dublin Declaration. These commitments tasked the OCEEA to engaging in relevant capacity building activities and encouraged participating States to promote transparency and accountability in the public sector.
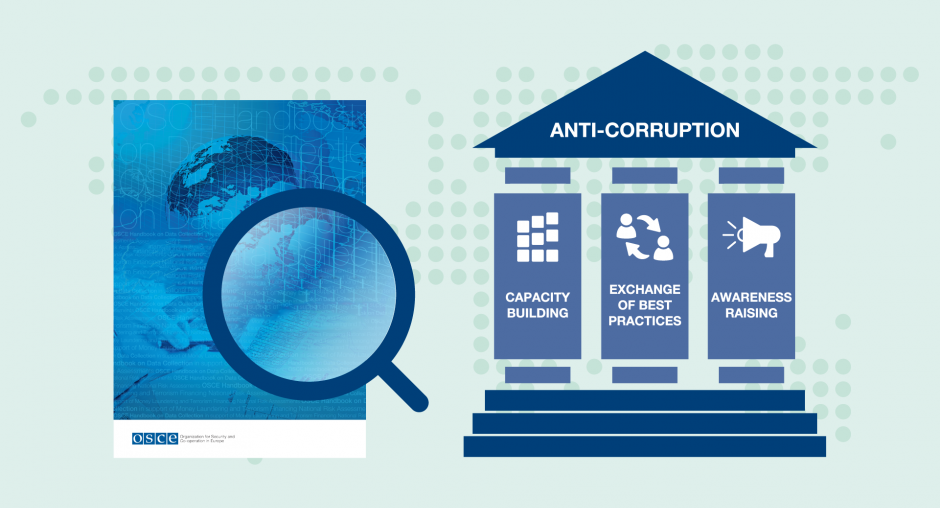
The OSCE supports concrete anti-corruption programmes and activities through capacity building and awareness-raising events, scoping and advisory missions, as well as activities aimed at strengthening institutional and legislative frameworks. Increasingly, the assistance is focusing on corruption prevention measures, asset recovery, anti-money laundering and countering terrorism financing through national risk assessments, sharing of experiences and best practices, and online training.
The OCEEA activities include:
- Promoting the ratification and implementation of the UN Convention against Corruption and the Financial Action Task Force’s Recommendations on anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism;
- Improving national anti-corruption, anti-money laundering and countering terrorism financing frameworks;
- Conducting capacity building through sharing the best practises and regional training activities for representatives of governments, the private sector and civil society;
- Developing mechanisms of information sharing to more effectively identify, trace, and suppress money laundering and the financing of terrorism;
- Promoting stolen asset recovery initiatives and strengthening international co-operation in financial investigations;
- Conducting national risk assessments, by which countries identify the threat of money laundering activity in their jurisdiction, examine the vulnerability of the country in its ability to prevent and intercept specific types of illicit financial activity.
- Providing tools and guidance for policy makers and practitioners on good governance issues through publications such as the OSCE Handbook on Combating Corruption, the OSCE Handbook on Data Collection in Support of Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing National Risk Assessments and OSCE online training modules on good governance and combating corruption.
- Producing policy recommendations and publications.
The OCEEA implements its anti-corruption activities in co-operation with OSCE Field Operations and many other partners, such as, UNODC, OECD, IACA and relevant national agencies.